Volumes of Solids of Revolution
This type of solid will be made up of one of three types of
elements—
Disks,
Washers, or
Cylindrical shells
—each of which requires a
different approach in setting up the definite integral to determine its
volume.
Disk method
If the axis of
revolution is the boundary of the plane region and the cross sections
are taken perpendicular to the axis of revolution, then you use the
disk method to find the volume of the solid. Because the cross section of a disk is a circle with area π
r2, the volume of each disk is its area times its thickness. If a disk is perpendicular to the
x-axis, then its radius should be expressed as a function of
x. If a disk is perpendicular to the
y-axis, then its radius should be expressed as a function of
y.
The volume (
V) of a solid generated by revolving the region bounded by
y =
f(x) and the
x-axis on the interval [
a, b] about the
x-axis is
If the region bounded by
x =
f(y) and the
y-axis on [
a, b] is revolved about the
y-axis, then its volume (
V) is
Note that
f(x) and
f(y) represent the radii of the disks or the distance between a point on the curve to the axis of revolution.
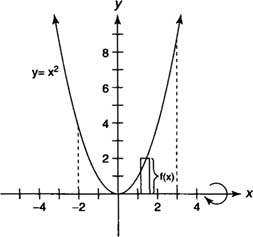
Example 1:
Find the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region bounded by
y =
x2 and the
x-axis on [−2,3] about the
x-axis.
Because the
x-axis is a boundary of the region, you can use the disk method (see Figure
1 ).
|
|
|
|
| Figure 1 | Diagram for Example 1. |
|
|
The volume (
V) of the solid is
Washer method
If
the axis of revolution is not a boundary of the plane region and the
cross sections are taken perpendicular to the axis of revolution, you
use the
washer method to find the volume of the solid.
Think of the washer as a “disk with a hole in it” or as a “disk with a
disk removed from its center.” If
R is the radius of the outer disk and
r is the radius of the inner disk, then the area of the washer is π
R2 – π
r2, and its volume would be its area times
its thickness. As noted in the discussion of the disk method, if a
washer is perpendicular to the
x-axis, then the inner and outer radii should be expressed as functions of
x. If a washer is perpendicular to the
y-axis, then the radii should be expressed as functions of
y.
The volume (
V) of a solid generated by revolving the region bounded by
y =
f(x) and
y =
g(x) on the interval [
a, b] where
f(x) ≥
g(x), about the
x-axis is
If the region bounded by
x =
f(y) and
x =
g(y) on [
a, b], where
f(y) ≥
g(y) is revolved about the
y-axis, then its volume (
V) is
Note again that
f(x) and
g(x) and
f(y) and
g(y) represent the outer and inner radii of the washers or the distance between a point on each curve to the axis of revolution.
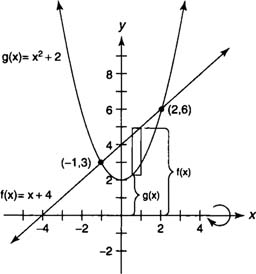
Example 2: Find the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region bounded by
y =
x2 + 2 and
y =
x + 4 about the
x-axis.
Because
y =
x2 + 2 and
y =
x + 4, you find that
The graphs will intersect at (–1,3) and (2,6) with x + 4 ≥
x2 + 2 on [–1,2] (Figure
2 ).
|
|
|
|
| Figure 2 | Diagram for Example 2. |
|
|
Because the
x-axis is not a boundary of the region, you can use the washer method, and the volume (
V) of the solid is
Cylindrical shell method
If the cross sections of the solid are taken parallel to the axis of revolution, then the
cylindrical shell method will be used to find the volume of the solid. If the cylindrical shell has radius
r and height
h, then its volume would be 2π
rh times its thickness. Think of the first part of this product, (2π
rh), as the area of the rectangle formed by cutting the
shell perpendicular to its radius and laying it out flat. If the axis
of revolution is vertical, then the radius and height should be
expressed in terms of
x. If, however, the axis of revolution is horizontal, then the radius and height should be expressed in terms of
y.
The volume (
V) of a solid generated by revolving the region bounded by
y =
f(x) and the
x-axis on the interval [
a,b], where
f(x) ≥ 0, about the
y-axis is
If the region bounded by
x =
f(y) and the
y-axis on the interval [
a,b], where
f(y) ≥ 0, is revolved about the
x-axis, then its volume (
V) is
Note that the
x and
y in the integrands represent the radii of the
cylindrical shells or the distance between the cylindrical shell and the
axis of revolution. The
f(x) and
f(y) factors represent the heights of the cylindrical shells.
Example 3: Find the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region bounded by
y =
x2 and the
x-axis [1,3] about the
y-axis.
In using the cylindrical shell method, the integral should be expressed in terms of
x because the axis of revolution is vertical. The radius of the shell is
x, and the height of the shell is
f(x) =
x2 (Figure
3 ).
|
|
|
|
| Figure 3 | Diagram for Example 3. |
|
|
The volume (
V) of the solid is


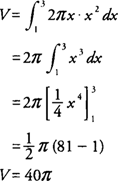



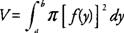


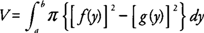
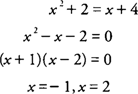
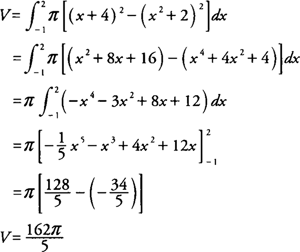
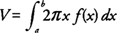
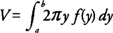


Thanks for such a great information.Mensuration is a very important topic of mathematics as it is very much related to our daily life like area and volume of different solid figures or area of plot,length and breadth of different object.It is interlinked with many real life problems.
ReplyDeleteicse textbooks for class 9