Mechanics
Engineering Mechanics
Engineering Mechanics is divided into two: Statics and Dynamics.Statics includes the following topics: resultant of force system; equilibrium of force system; cables; friction; trusses; frames; centroid; center of gravity; and moment of inertia.
Dynamics will cover the following topics: kinematics, dynamics, kinetics, work-energy equation, impulse and momentum, and mechanical vibrations.
Principles of Statics
Statics is a branch of mechanics which studies the effects and distribution of forces of rigid bodies which are and remain at rest. In this area of mechanics, the body in which forces are acting is assumed to be rigid. The deformation of the body is treated in Mechanics and Strength of Materials.Topics in Statics:
- Resultant of Force System
- Equilibrium of Force System
- Analysis of Trusses
- Cables
- Friction
- Centroids and Centers of Mass
- Moments of Inertia
Advances in thermodynamics led to the development of industrialization; and
Advances in Mechanics inspired the development of calculus
Archimedes' screw, a simple machine for lifting
Mechanics (Greek) is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment.
The major division of the mechanics discipline separates:
Prof. Walter Lewin explains Newton's law of gravitation in MIT course 8.01
- Analytical mechanics
- Applied mechanics
- Dynamics
- Engineering
- Index of engineering science and mechanics articles
- Kinematics
- Kinetics
- Statics
Classical Mechanics:
The following are described as forming Classical mechanics:
- Hamiltonian mechanics, a theoretical formalism, based on the principle of conservation of energy
- Lagrangian mechanics, another theoretical formalism, based on the principle of the least action
- Celestial mechanics, the motion of bodies in space: planets, comets, stars, galaxies, etc.
- Astrodynamics, spacecraft navigation, etc.
- Solid mechanics, elasticity, the properties of deformable bodies.
- Statics, semi-rigid bodies in mechanical equilibrium
- Fluid mechanics, the motion of fluids
- Soil mechanics, mechanical behavior of soils
- Continuum mechanics, mechanics of continua (both solid and fluid)
- Hydraulics, mechanical properties of liquids
- Fluid statics, liquids in equilibrium
- Biomechanics, solids, fluids, etc. in biology
- Biophysics, physical processes in living organisms
- Statistical mechanics, assemblies of particles too large to be described in a deterministic way
Quantum mechanics
The following are categorized as being part of Quantum mechanics:
- Particle physics, the motion, structure, and reactions of particles
- Nuclear physics, the motion, structure, and reactions of nuclei
- Condensed matter physics, quantum gases, solids, liquids, etc.
- Quantum statistical mechanics, large assemblies of particles
- Applied Mechanics Division, American Society of Mechanical Engineers
- Fluid Dynamics Division, American Physical Society
- Institution of Mechanical Engineers is the United Kingdom's qualifying body for Mechanical Engineers and has been the home of Mechanical Engineers for over 150 years.
This parabola-shaped lava flow illustrates the application of Mathematics in Physics – in this case,
Galileo's law of falling bodies

The distinction between Mathematics and Physics is clear-cut,
but not always obvious, especially in Mathematical Physics
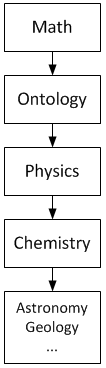
Mathematics and Ontology are used in Physics.
Physics is used in Chemistry and Cosmology
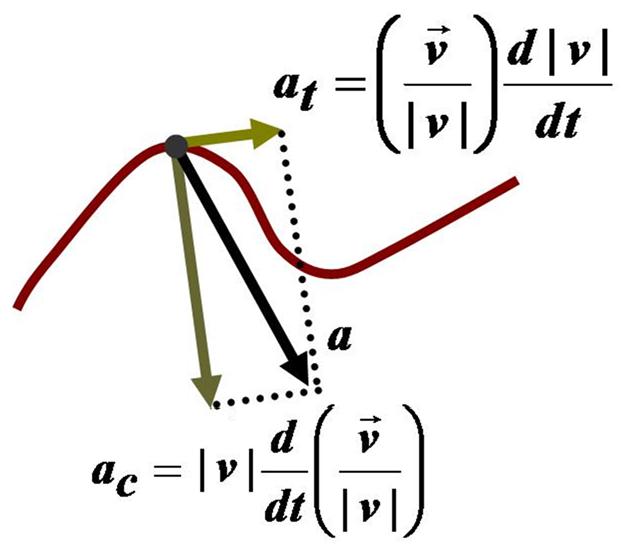
Physics involves modeling the natural world with theory, usually quantitative. Here, the path of a particle is modeled with the mathematics of calculus to explain its behavior: the purview of the branch of physics known as mechanics
Physics 1

The distinction between Mathematics and Physics is clear-cut,
but not always obvious, especially in Mathematical Physics

Mathematics and Ontology are used in Physics.
Physics is used in Chemistry and Cosmology
Physics involves modeling the natural world with theory, usually quantitative. Here, the path of a particle is modeled with the mathematics of calculus to explain its behavior: the purview of the branch of physics known as mechanics
Physics 1
Mechanics Overview
Mechanics is the branch of Physics dealing with the study of
motion.
No matter what your interest in science or engineering,
mechanics will be important for you - motion is a fundamental idea in
all of science.
Mechanics can be divided into 2 areas -
- kinematics, dealing with describing motions, and
- dynamics, dealing with the causes of motion.
Physics 1 Mechanics topics include:
- Kinematics
- Dynamics
- Newton's Laws
- Momentum and Conservation of Momentum (in One Dimension)
- Energy and Conservation of Energy
Common phrases or words used in questions
- particle: a point mass
- body: same as a particle (not of the human variety)
- light inextensible string: a string with negligible mass that does not stretch
Guide lines on resolving:
Always aim to resolve in the direction that an object is moving.
If it is moving up a plane, resolve up the plane, if it is moving down the plane then resolve down the plane.
If you resolve in the opposite direction to motion then you will
generally find yourself getting into all sorts of problems over
acceleration having to be negative.
State the direction you are resolving by using R(left), R(up the
plane) etc. Arrows inside the brackets can be used. It makes it clear to
the person marking your work what you are intending to do.
Simple machine
A simple machine is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that provide mechanical advantage (also called leverage).
Usually the term refers to the six classical simple machines which were defined by Renaissance scientists:
A simple machine is an elementary device that has a specific movement (often called a mechanism), which can be combined with other devices and movements to form a machine.
A simple machine is an elementary device that has a specific movement (often called a mechanism), which can be combined with other devices and movements to form a machine.
Between the simple machines and complex assemblies, several intermediate
classes can be defined, which may be termed "compound machines" or "machine elements".
The mechanical advantage of a compound machine is simply the product of
the mechanical advantages of the simple machines of which it is
composed.


No comments:
Post a Comment